概要
最近Spring Frameworkに影響を与える複数の脆弱性が公表されました。3月の初め以降に発表された4つの脆弱性の中では、2022年3月31日に明らかにされたCVE-2022-22965が最も影響が重大で、SpringShellと呼ばれています。
SpringShell脆弱性は、影響を受けたシステムに攻撃者が未認証でリモートコード実行(RCE)を行うことを可能にします。SpringShell脆弱性に関する分析の全文は、Unit 42 脅威に関する情報をご覧ください。
Prisma Cloudは、あらゆるクラウド資産で最近のすべてのSpringShell脆弱性を検出できます。影響を受けたインスタンスを検出するだけでなく、Prisma Cloudは脆弱なコンテナイメージの実行を防いだり停止したりもできます。また、Prisma Cloudはさまざまな機能やエクスプロイト後の手法により脆弱性のエクスプロイトを防止します。
背景
Spring Frameworkは、Javaプラットフォームのための包括的なオープンソース アプリケーション フレームワークです。その強力な機能と使いやすさから、業界で幅広く利用されています。Spring Coreコンポーネントはフレームワークの中核となるもので、Inversion of Control (制御の反転)や依存性注入などの強力な機能を提供しています。これには、core、beans、context、Spring Expression Language (SpEL)モジュールが含まれています。
Spring Cloud Functionは、ビジネスロジックの開発ライフサイクルを促進し、サーバーレスプロバイダ間で統一されたプログラミングモデルをサポートするために設計されたプロジェクトです。Spring Expression Language (SpEL)は、メソッドの呼び出しや基本的な文字列テンプレート機能を含むUnified ELを利用し、実行時のオブジェクトのクエリと操作をサポートします。
3月の初め以降、Spring Frameworkに関するCVEが合計4つ公表されています。
- CVE-2022-22947 - Spring Cloud Gateway - リモートコード実行
- CVE-2022-22950 - Spring Expression Language (SpEL) - サービス拒否
- CVE-2022-22963 - Spring Cloud Function - リモートコード実行
- CVE-2022-22965 - Spring Core - リモートコード実行
Prisma Cloudの検出機能
Prisma Cloudのユーザーは、CVE-2022-22963またはCVE-2022-22965のいずれかの脆弱性の影響を受けたソフトウェアコンポーネントを検出できます。Prisma Cloud Intelligence Stream (IS)は、公式なベンダーフィードからの脆弱性情報が含まれるよう、自動的に更新されます。これにより、Prisma CloudではLinuxディストリビューションやアプリケーションメンテナによるあらゆる更新や分析を直接反映でき、影響を受けたあらゆる機能、イメージ、ホストを検出できます。
また、Prisma Cloudではシステムやアプリケーションに影響を与えるものでありながら、CVE追跡番号を割り当てられてこなかった、またはまだ割り当てられていない、業界で知られた厳選された一連の脆弱性を対象としたPRISMA IDも採用しています。 業界で知られているもののCVE追跡番号をまだ割り当てられていない脆弱性はPrisma Cloudのクラウド セキュリティ リサーチ チーム(CSRT)で分析され、Prisma CloudのISに追加されます。業界で知られた脆弱性を追跡するPRISMA-IDにより、Prisma Cloudでは短時間でクライアント環境に脆弱性検出ルールをプッシュできます。多くの場合、CVE情報が公開されるよりも早くプッシュが可能です。
その典型例であるSpringShell脆弱性(CVE-2022-22965)は、Prisma IDのルールが公開されたCVE情報よりも早いペースで脆弱性を検出している一例です。SpringShell CVE (CVE-2022-22965)は2022年3月31日に公開されましたが、Prisma CloudのCSRTはPrisma IDルール「PRISMA-2022-0130」を2022年3月30日に公開しています。つまり、Prisma Cloudのクラウドワークロード保護(CWP)モジュールのクライアントは、その脆弱性のその正式リリースの何時間も前にCVE-2022-22965を検出できたことになります。
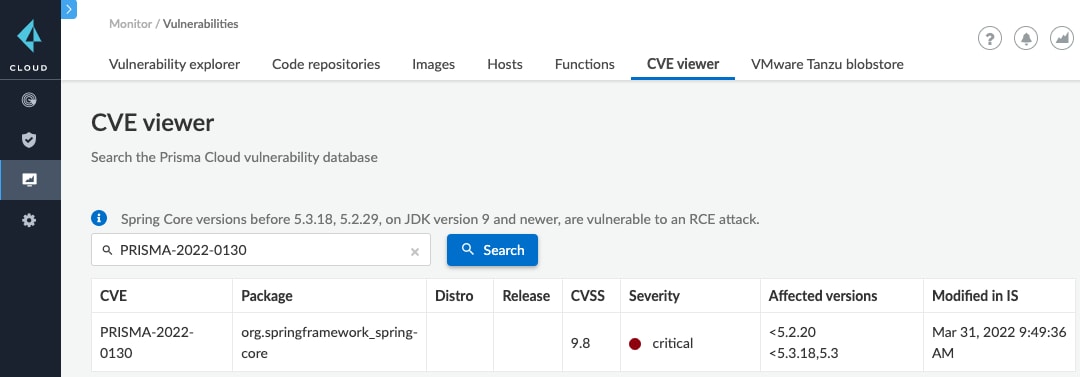
このリスクを抱えるホストがないか環境をクエリ
Prisma CloudのRQL (Resource Query Language)では、影響を受けたリソースを迅速かつ簡単にクエリできます。ユーザーは、Prismaプラットフォームの機能を使用して脆弱性のある資産を分離し、インターネットに公開されトラフィックを受信している資産を探すことでそれらをさらに優先順位付けできます。
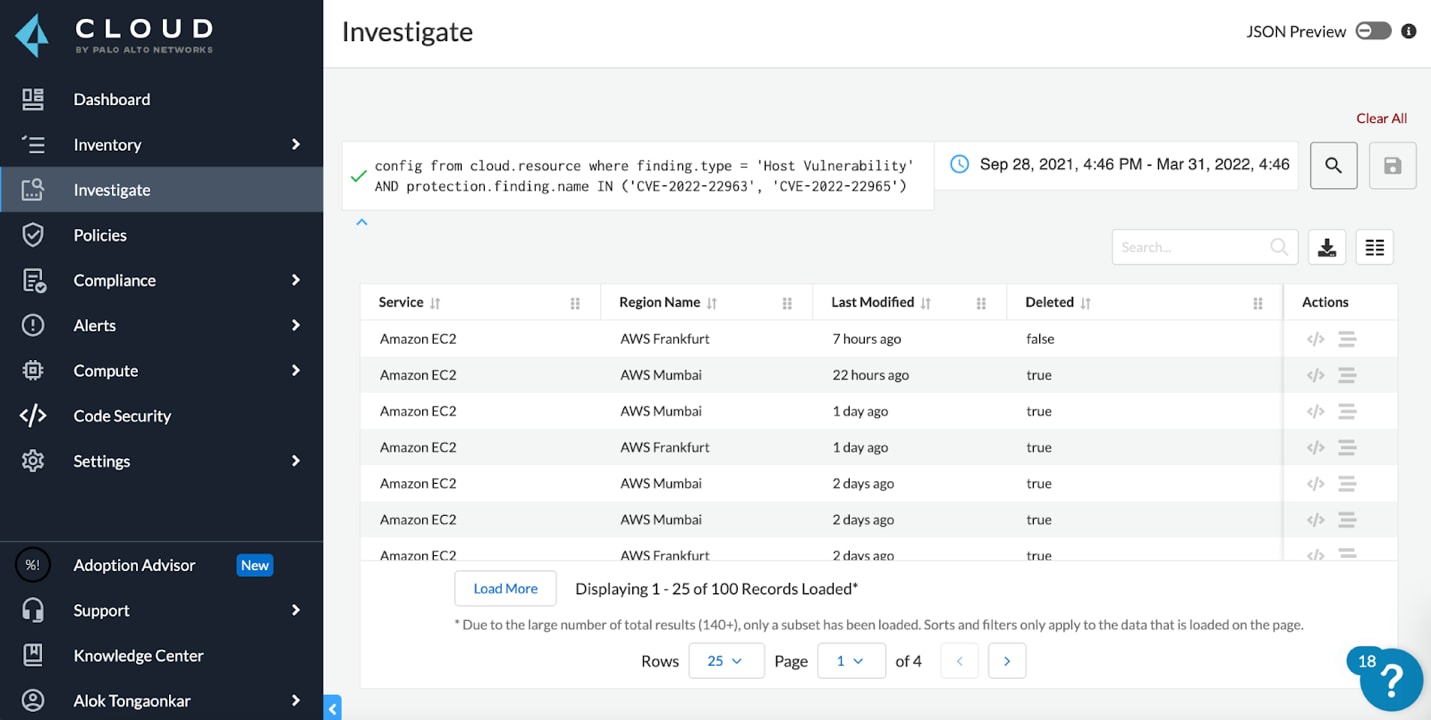
CVE-2022-22963またはCVE-2022-22965という具体的な脆弱性を持つクラウド内のホストを把握するには以下をクエリします。
|
1 |
config from cloud.resource where finding.type = 'Host Vulnerability' AND protection.finding.name IN ('CVE-2022-22963', 'CVE-2022-22965') |
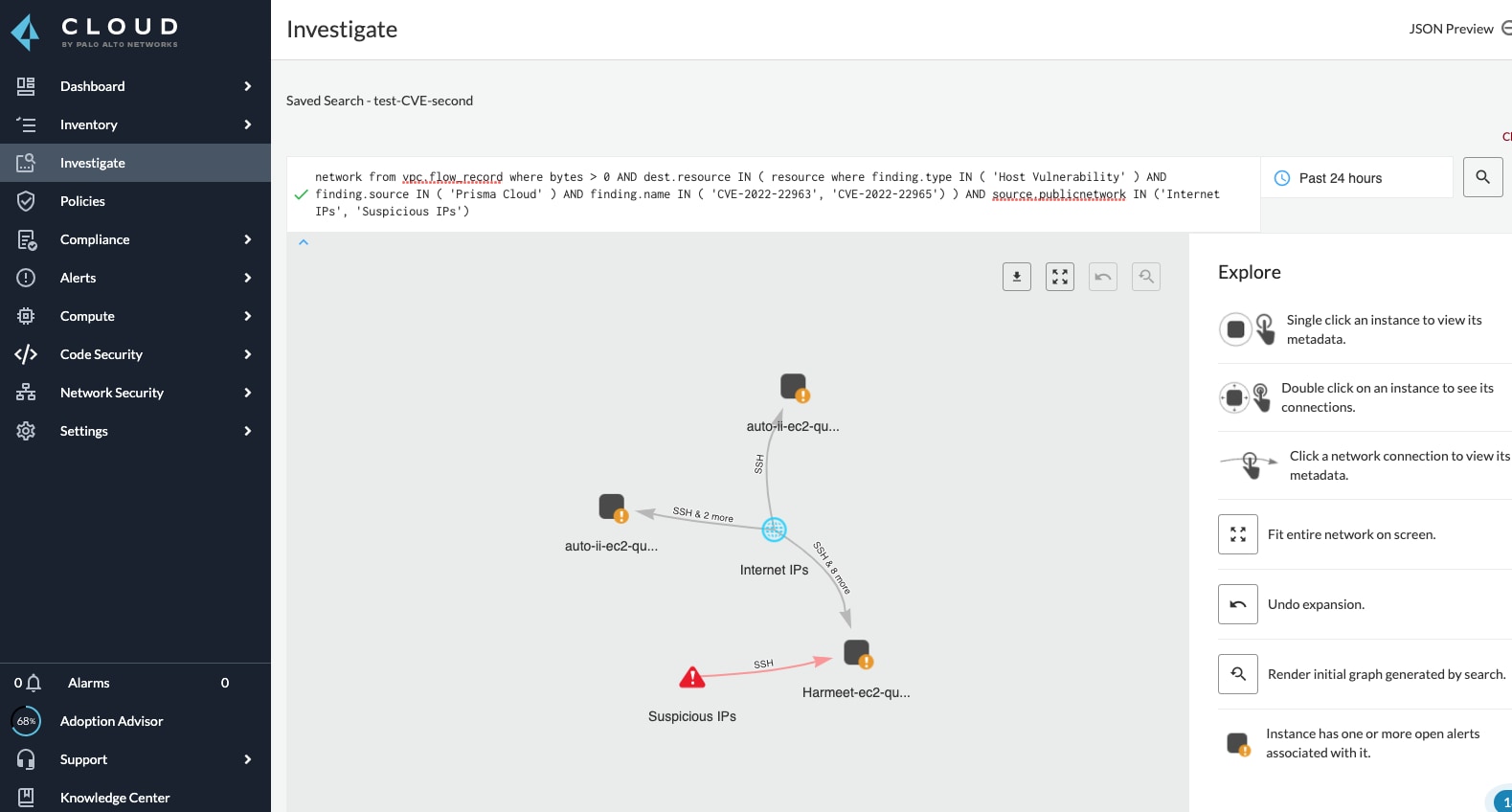
クラウドでトラフィックを受信しており、CVE-2022-22963またはCVE-2022-22965という具体的な脆弱性を持つインターネットに公開されたホストを把握するには以下をクエリします。
|
1 |
network from vpc.flow_record where bytes > 0 AND destination.resource IN ( resource where finding.type IN ( 'Host Vulnerability' ) AND finding.source IN ( 'Prisma Cloud' ) AND finding.name IN ('CVE-2022-22963', 'CVE-2022-22965') ) AND source.publicnetwork IN ('Internet IPs', 'Suspicious IPs' |
WAASが有効となっているPrisma Cloudユーザーは、弊社がSpringShellについて分析したエクスプロイト(CVE-2022-22965)の大半からApp Firewall Code Injection検出機能によって保護されます。
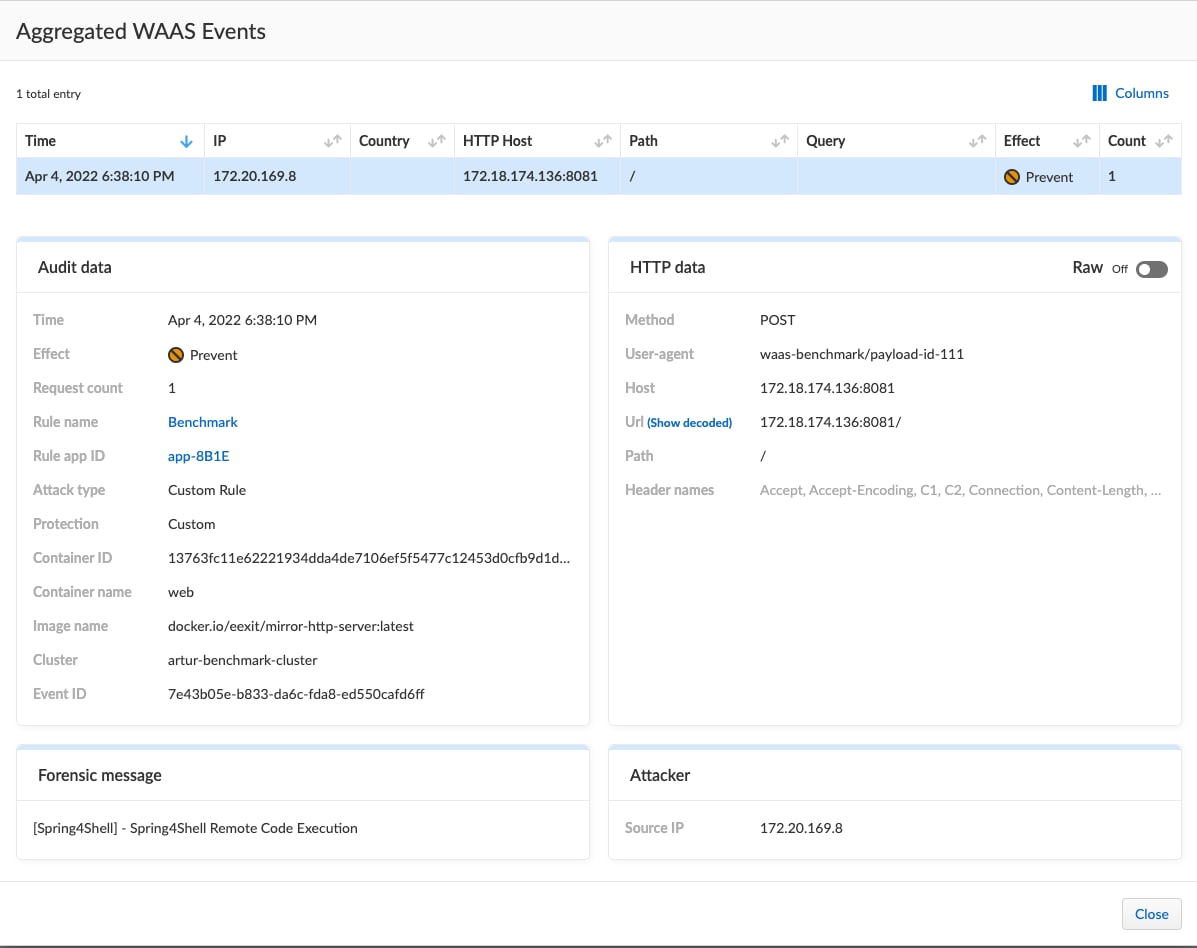
CVE-2022-22965 (Spring4Shell)とCVE-2022-22963 (Spring Cloud Function)に対し、それらの回避も含めより正確に対応するためにカスタムルールを作成しました。WAASが有効となっているユーザーは、下記の新しいカスタムルールを保護のためにインポートできます。
WAASバージョン22.01.839以上に対応したルールは次の通りです。
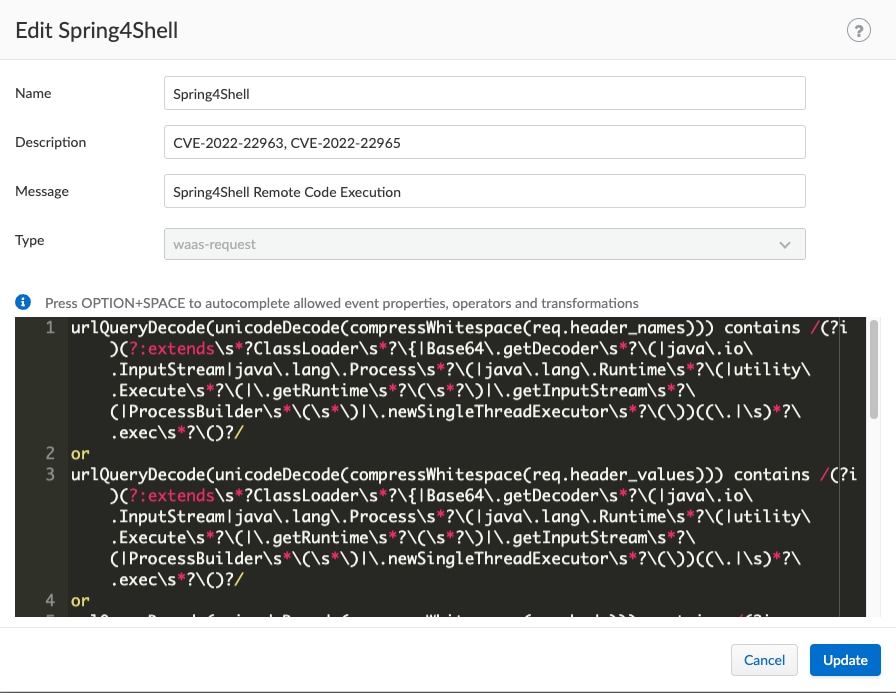
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
urlQueryDecode(unicodeDecode(compressWhitespace(req.header_names))) contains /(?i)(?:extends\s*?ClassLoader\s*?\{|Base64\.getDecoder\s*?\(|java\.io\.InputStream|java\.lang\.Process\s*?\(|java\.lang\.Runtime\s*?\(|utility\.Execute\s*?\(|\.getRuntime\s*?\(\s*?\)|\.getInputStream\s*?\(|ProcessBuilder\s*\(\s*\)|\.newSingleThreadExecutor\s*?\(\))((.|\s)*?\.exec\s*?\()?/ or urlQueryDecode(unicodeDecode(compressWhitespace(req.header_values))) contains /(?i)(?:extends\s*?ClassLoader\s*?\{|Base64\.getDecoder\s*?\(|java\.io\.InputStream|java\.lang\.Process\s*?\(|java\.lang\.Runtime\s*?\(|utility\.Execute\s*?\(|\.getRuntime\s*?\(\s*?\)|\.getInputStream\s*?\(|ProcessBuilder\s*\(\s*\)|\.newSingleThreadExecutor\s*?\(\))((.|\s)*?\.exec\s*?\()?/ or urlQueryDecode(unicodeDecode(compressWhitespace(req.body))) contains /(?i)(?:extends\s*?ClassLoader\s*?\{|Base64\.getDecoder\s*?\(|java\.io\.InputStream|java\.lang\.Process\s*?\(|java\.lang\.Runtime\s*?\(|utility\.Execute\s*?\(|\.getRuntime\s*?\(\s*?\)|\.getInputStream\s*?\(|ProcessBuilder\s*\(\s*\)|\.newSingleThreadExecutor\s*?\(\))((.|\s)*?\.exec\s*?\()?/ or urlQueryDecode(unicodeDecode(compressWhitespace(req.body_param_values))) contains /(?i)(?:extends\s*?ClassLoader\s*?\{|Base64\.getDecoder\s*?\(|java\.io\.InputStream|java\.lang\.Process\s*?\(|java\.lang\.Runtime\s*?\(|utility\.Execute\s*?\(|\.getRuntime\s*?\(\s*?\)|\.getInputStream\s*?\(|ProcessBuilder\s*\(\s*\)|\.newSingleThreadExecutor\s*?\(\))((.|\s)*?\.exec\s*?\()?/ or urlQueryDecode(unicodeDecode(compressWhitespace(req.query_param_names))) contains /(?i)(?:extends\s*?ClassLoader\s*?\{|Base64\.getDecoder\s*?\(|java\.io\.InputStream|java\.lang\.Process\s*?\(|java\.lang\.Runtime\s*?\(|utility\.Execute\s*?\(|\.getRuntime\s*?\(\s*?\)|\.getInputStream\s*?\(|ProcessBuilder\s*\(\s*\)|\.newSingleThreadExecutor\s*?\(\))((.|\s)*?\.exec\s*?\()?/ or urlQueryDecode(unicodeDecode(compressWhitespace(req.query_param_values))) contains /(?i)(?:extends\s*?ClassLoader\s*?\{|Base64\.getDecoder\s*?\(|java\.io\.InputStream|java\.lang\.Process\s*?\(|java\.lang\.Runtime\s*?\(|utility\.Execute\s*?\(|\.getRuntime\s*?\(\s*?\)|\.getInputStream\s*?\(|ProcessBuilder\s*\(\s*\)|\.newSingleThreadExecutor\s*?\(\))((.|\s)*?\.exec\s*?\()?/ |
WAASバージョン21.08.525以上に対応したルールは次の通りです。
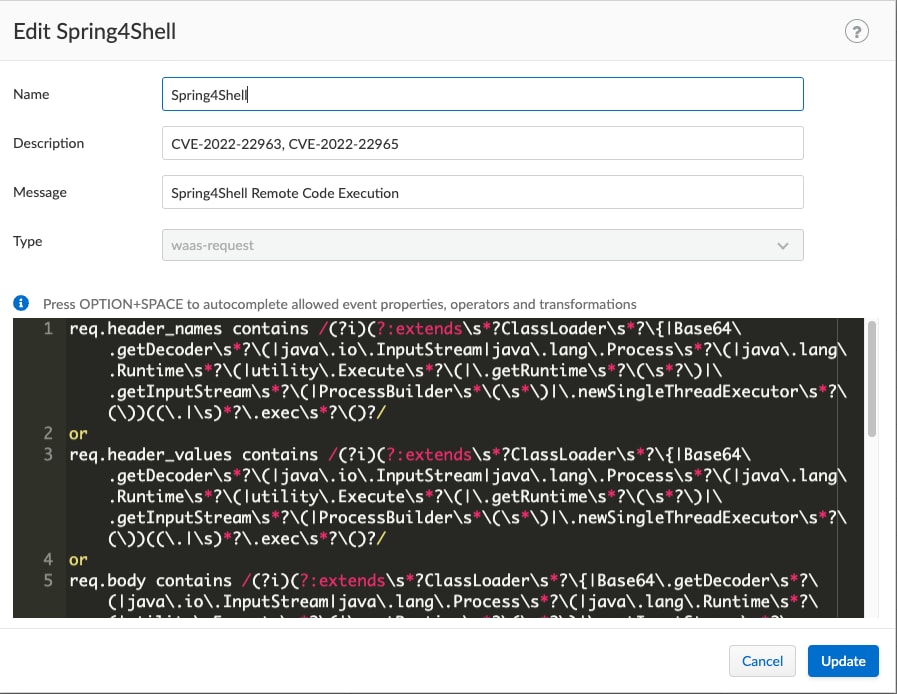
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
req.header_names contains /(?i)(?:extends\s*?ClassLoader\s*?\{|Base64\.getDecoder\s*?\(|java\.io\.InputStream|java\.lang\.Process\s*?\(|java\.lang\.Runtime\s*?\(|utility\.Execute\s*?\(|\.getRuntime\s*?\(\s*?\)|\.getInputStream\s*?\(|ProcessBuilder\s*\(\s*\)|\.newSingleThreadExecutor\s*?\(\))((.|\s)*?\.exec\s*?\()?/ or req.header_values contains /(?i)(?:extends\s*?ClassLoader\s*?\{|Base64\.getDecoder\s*?\(|java\.io\.InputStream|java\.lang\.Process\s*?\(|java\.lang\.Runtime\s*?\(|utility\.Execute\s*?\(|\.getRuntime\s*?\(\s*?\)|\.getInputStream\s*?\(|ProcessBuilder\s*\(\s*\)|\.newSingleThreadExecutor\s*?\(\))((.|\s)*?\.exec\s*?\()?/ or req.body contains /(?i)(?:extends\s*?ClassLoader\s*?\{|Base64\.getDecoder\s*?\(|java\.io\.InputStream|java\.lang\.Process\s*?\(|java\.lang\.Runtime\s*?\(|utility\.Execute\s*?\(|\.getRuntime\s*?\(\s*?\)|\.getInputStream\s*?\(|ProcessBuilder\s*\(\s*\)|\.newSingleThreadExecutor\s*?\(\))((.|\s)*?\.exec\s*?\()?/ or req.body_param_values contains /(?i)(?:extends\s*?ClassLoader\s*?\{|Base64\.getDecoder\s*?\(|java\.io\.InputStream|java\.lang\.Process\s*?\(|java\.lang\.Runtime\s*?\(|utility\.Execute\s*?\(|\.getRuntime\s*?\(\s*?\)|\.getInputStream\s*?\(|ProcessBuilder\s*\(\s*\)|\.newSingleThreadExecutor\s*?\(\))((.|\s)*?\.exec\s*?\()?/ or req.query_param_names contains /(?i)(?:extends\s*?ClassLoader\s*?\{|Base64\.getDecoder\s*?\(|java\.io\.InputStream|java\.lang\.Process\s*?\(|java\.lang\.Runtime\s*?\(|utility\.Execute\s*?\(|\.getRuntime\s*?\(\s*?\)|\.getInputStream\s*?\(|ProcessBuilder\s*\(\s*\)|\.newSingleThreadExecutor\s*?\(\))((.|\s)*?\.exec\s*?\()?/ or req.query_param_values contains /(?i)(?:extends\s*?ClassLoader\s*?\{|Base64\.getDecoder\s*?\(|java\.io\.InputStream|java\.lang\.Process\s*?\(|java\.lang\.Runtime\s*?\(|utility\.Execute\s*?\(|\.getRuntime\s*?\(\s*?\)|\.getInputStream\s*?\(|ProcessBuilder\s*\(\s*\)|\.newSingleThreadExecutor\s*?\(\))((.|\s)*?\.exec\s*?\()?/ |
要約
SpringShellは幅広く利用されているSpring Frameworkの深刻な脆弱性でした。SpringShellには正式にCVE-2022-22965が割り当てられ、2022年3月31日にパッチがリリースされました。さらに、2022年3月の初め以降、Spring Cloud Gateway、Spring Expression Language (SpEL)、Spring Cloud Functionのコンポーネントに影響を及ぼす3つの脆弱性がこのほかに公表されています。
Prisma Cloudは、デプロイメント内のすべての脆弱なインスタンスの検出を支援します。Prisma Cloudは、この問題に対して脆弱なすべてのイメージやホストの実行を完全に防ぐよう設定することもできます。
SpringShell脆弱性に関する詳細な技術分析については、パロアルトネットワークスのUnit 42の脅威に関する情報を参照してください。